Lesson 4: Choices for Treating Kidney Failure (The Basics)
The content of this lesson, Choices for Treating Kidney Failure (The Basics), meets the needs of qualified providers seeking to deliver the Kidney Disease Education (KDE) Services benefit, as defined by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (beneficiaries must have an eGFR of 29 or lower).
Lesson Objectives
By the end of each session, participants will be able to:
- Identify the four treatment choices for kidney failure
- State how hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis differ in frequency of treatment
Session Starter
There is a lot to know about the different treatments for kidney failure. What questions do you have? (Or ask what they have seen in their own community. Do they know people on dialysis? What have they heard about it?)
Topics & Points to Cover
- You have treatment choices, and you can change your mind.
- No renal replacement therapy also known as conservative management
- Active medical care without RRT
- Palliative care when necessary
- Complications can be managed, but can’t compensate for uremia
- End of life choices – living will – telling family
- Can change your mind
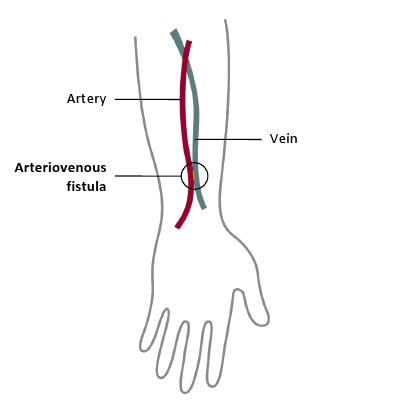
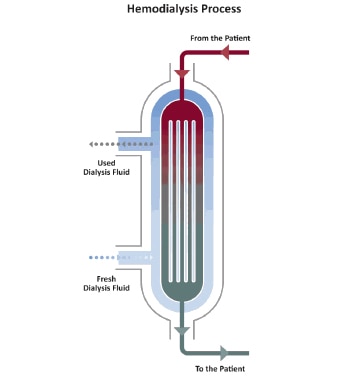
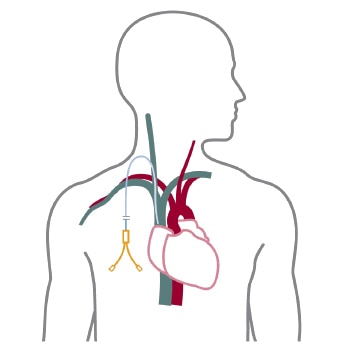
- Hemodialysis(HD)
- Two types
- In-center (most common)
- Home hemo: treatments are done at home, requires assistance, you have more control, can be harder on the helpers.
- How it works
- PROs and CONs
- The diet (in-center is most restrictive, only 3 times/week, build up between treatments)
- Lifestyle: social aspects
- Safety/infection
- Two types
- Peritoneal dialysis (PD)
-
Two types
- Continuous ambulatory PD
- Continuous cycling PD
- How it works
- PROs and CONs
- Storage space for supplies (delivered monthly)
- Diet (blood is cleaned every day, diet is less restrictive)
- Safety/infection control
-
Two types
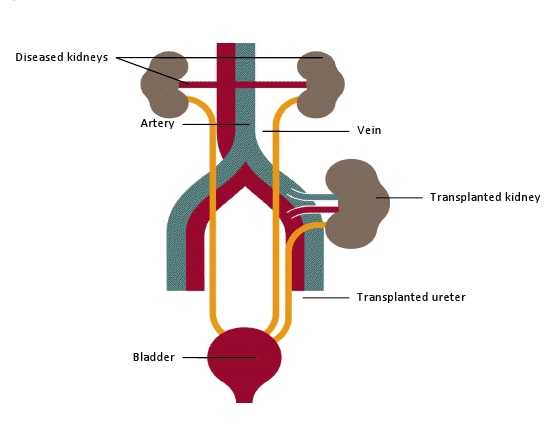
- Kidney transplant
- Types
- Deceased or living donor
- Eligibility
- Transplant evaluation
- Waiting list
- Still MUST take medications including anti-rejection medications
-
PROs and CONs
- The diet (least restrictive)
- Types
- Cultural aspects of different choices
- Be sensitive to your target audiences cultural beliefs in regards to all of the available options
Materials/Content for Learners
- Choosing a Treatment for Kidney Failure
Background/Clinical Information for Educators
- NIDDK videos:
- Hemodialysis
- Peritoneal Dialysis
- Kidney Transplant
Sample Outcome Assessment Questions
- What happens if a person chooses not to go on dialysis?
- What are the pros and cons of kidney transplant as an option for treatment of kidney failure?
Other outcomes:
- Patient lists the four treatment choices for kidney failure.
- Patient states frequency of HD and frequency of PD.
- Patient indicates how food choices for different treatments may change.
- Patient states what he/she will do with information from today’s session.
Additional Resources for Download
These images are available free of charge to download and include in your patient education materials.
-
A schematic showing a transplanted kidney placed in the groin area. Native kidneys usually are not removed.
Download (JPEG, <1 MB)
-
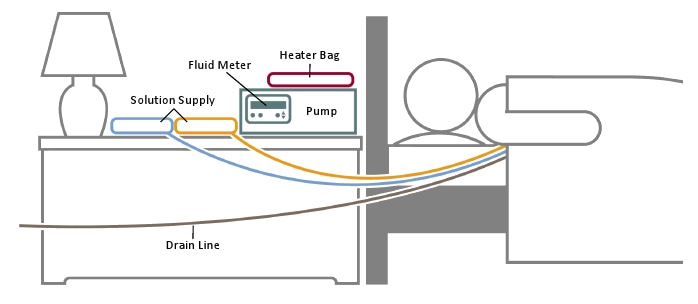
A schematic of a continuous cycler-assisted peritoneal dialysis exchange while person is sleeping.
Download (JPEG, <1 MB)
-
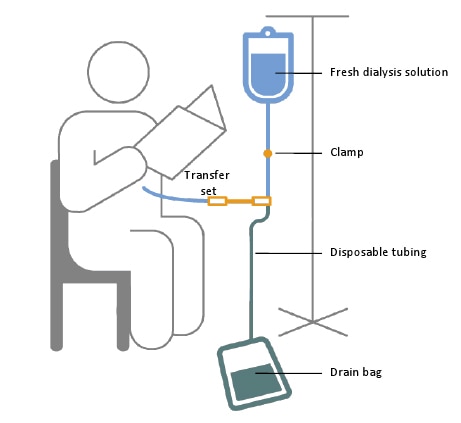
A schematic of a person receiving continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis exchange while reading.
Download (JPEG, <1 MB)
-
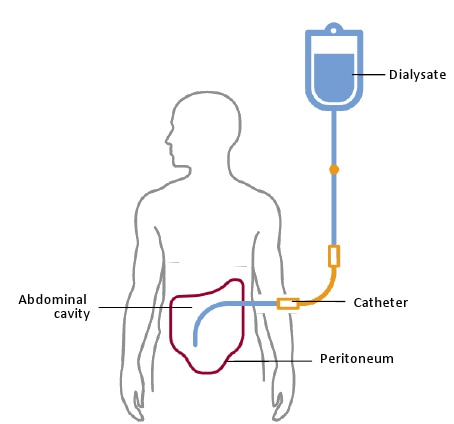
A schematic showing that the peritoneal membrane is the semipermeable “filter” in peritoneal dialysis.
Download (JPEG, <1 MB)