Definition & Facts of Kidney Infection (Pyelonephritis)
In this section:
- What is a kidney infection?
- How common are kidney infections?
- Who is more likely to develop a kidney infection?
- What are the complications of kidney infections?
What is a kidney infection?
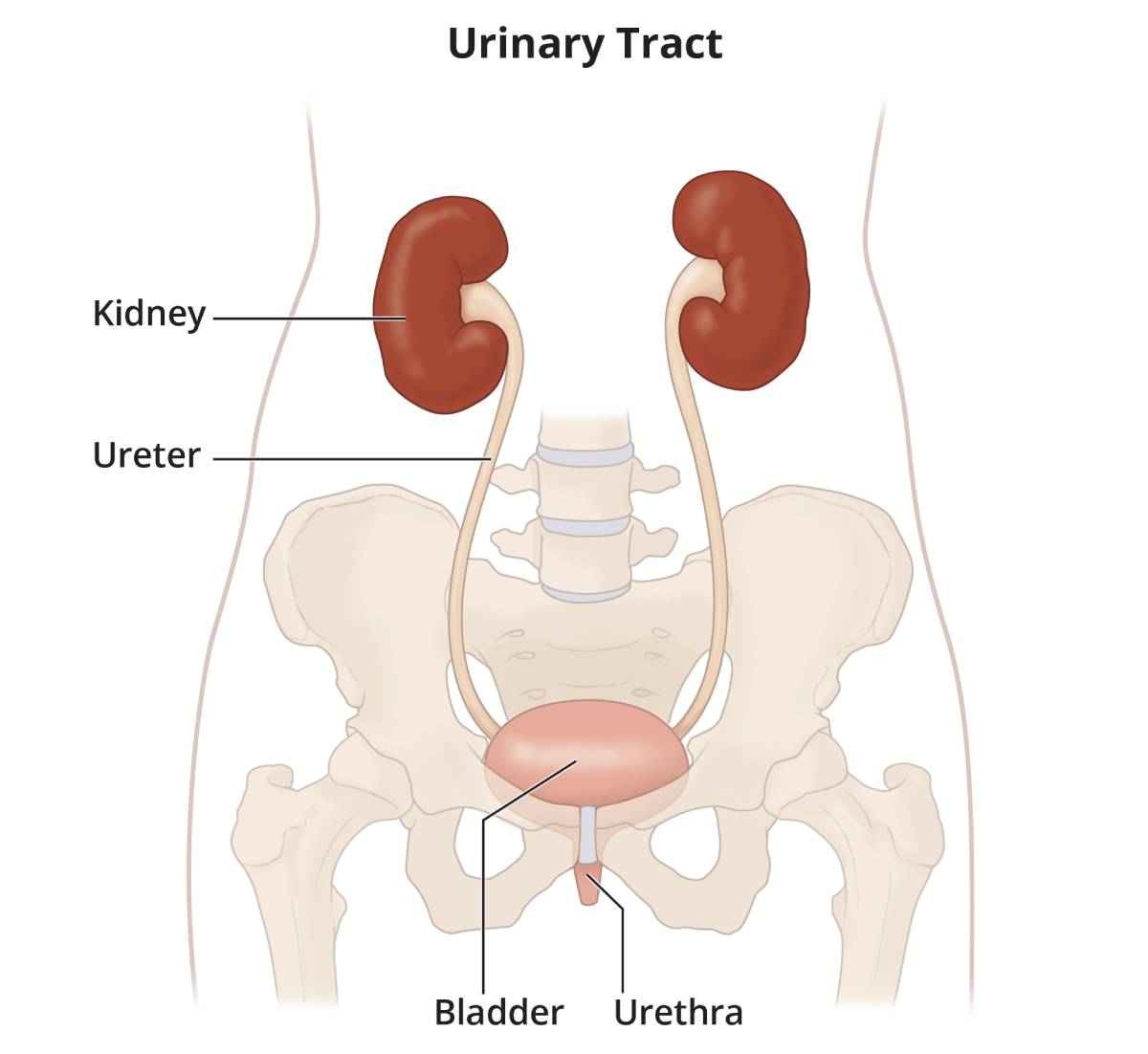
A kidney infection is a type of urinary tract infection (UTI). Most kidney infections are caused by bacteria or viruses that first infect your lower urinary tract, usually your bladder. Then, the infection moves up your ureters to one or both of your kidneys. The kidneys are part of the upper urinary tract. Kidney infections can be very painful and cause serious health problems.
If you have symptoms of a bladder infection, see a health care professional. You may need treatment to prevent the infection from spreading to your kidneys.
Does kidney infection have another name?
A kidney infection is also called pyelonephritis.
How common are kidney infections?
Kidney infections lead to about 250,000 office visits and 200,000 hospital admissions in the United States each year.1
Who is more likely to develop a kidney infection?
 Kidney infections are more common in females than males and are common during pregnancy.
Kidney infections are more common in females than males and are common during pregnancy.
You are more likely to develop a kidney infection if you
- are female
- have a current or recent bladder infection
- are pregnant
- have a urinary tract blockage, such as a kidney stone or enlarged prostate
- have a urinary tract problem such as vesicoureteral reflux, which is more common in children
- have diabetes or problems with your immune system
- have a spinal cord injury or nerve damage around the bladder
- have trouble emptying your bladder completely, called urinary retention
What are the complications of kidney infections?
When diagnosed early and treated properly, most kidney infections don’t lead to complications. In rare cases, kidney infections may cause
- high blood pressure
- kidney failure
- kidney scarring, which can lead to chronic kidney disease
- sepsis
Your chance of a complication is slightly greater if you
- are male
- are older or frail due to weakened strength or other problems of aging
- are pregnant
- have a problem with the structure of your urinary tract
- have had repeat kidney infections
- have certain health conditions, such as diabetes, kidney disease, or sickle cell disease
- have a weakened immune system or have had an organ transplant
Reference
This content is provided as a service of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
(NIDDK), part of the National Institutes of Health. NIDDK translates and disseminates research findings to increase knowledge and understanding about health and disease among patients, health professionals, and the public. Content produced by NIDDK is carefully reviewed by NIDDK scientists and other experts.

