Definition & Facts for Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency
In this section:
What is EPI?
Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) is a condition in which your small intestine can’t digest food completely because of problems with digestive enzymes from your pancreas. EPI often develops slowly, over many years.
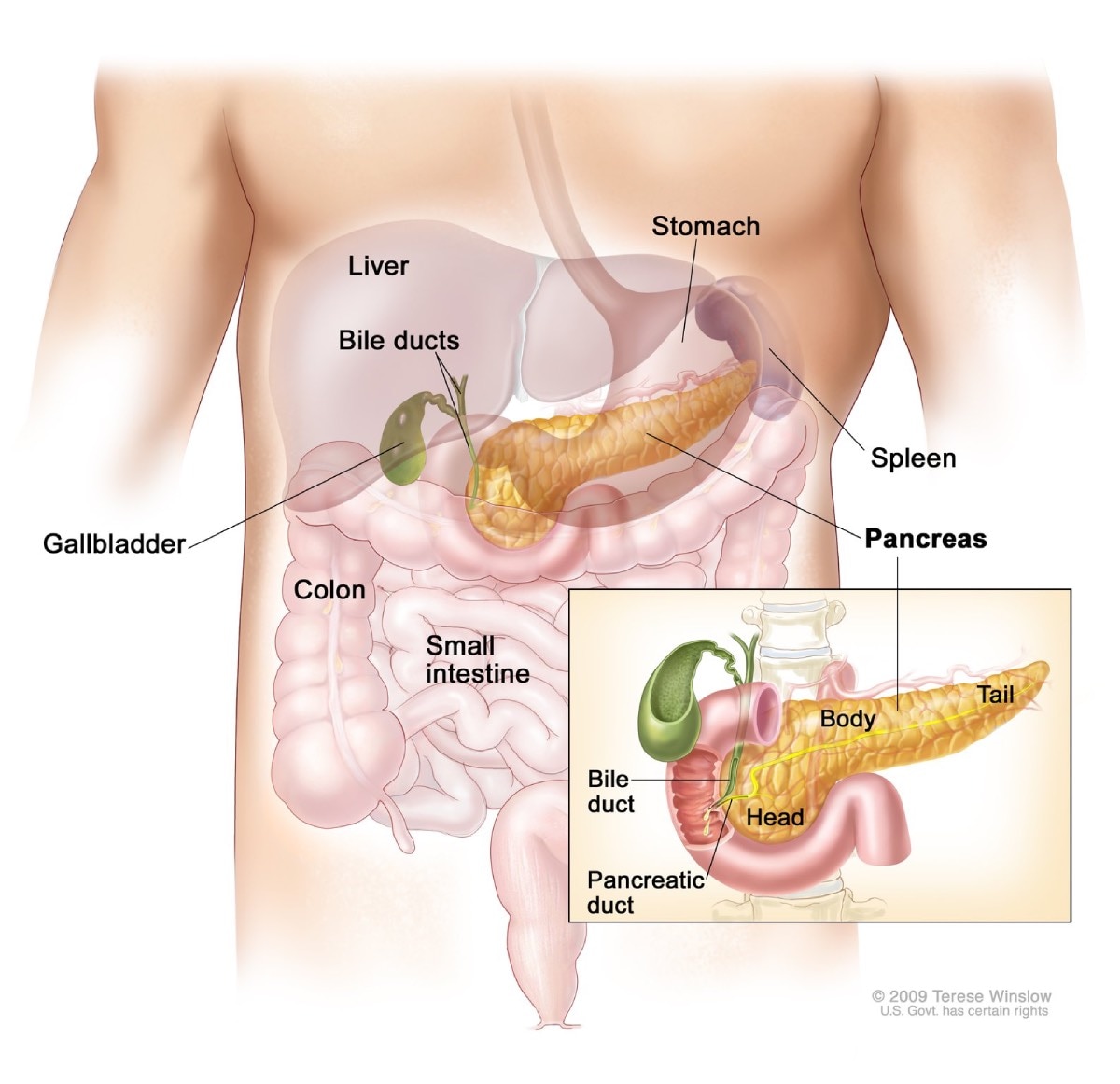
The pancreas is a large gland behind your stomach. The pancreas is both
- an endocrine gland that makes hormones
- an exocrine gland that makes digestive juice containing enzymes
The pancreas delivers the digestive juice to the small intestine through a single duct. In the small intestine, the enzymes from the pancreas help digest food, breaking down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
You may develop EPI if
- the amount of enzymes your pancreas makes is severely reduced
- not enough enzymes reach your small intestine
- other problems prevent the enzymes from mixing with food or otherwise working well
How common is EPI?
EPI is rare. However, problems with enzymes from the pancreas occur more often in people with certain health conditions.
Although study results vary, experts think problems with enzymes from the pancreas may occur in1
- 30% to 90% of people with chronic pancreatitis
- 80% to 90% of people with cystic fibrosis
Less commonly, problems with enzymes in the pancreas may occur in people who have
- pancreatic cancer that has not been removed by surgery
- type 1 diabetes or type 2 diabetes
- inflammatory bowel disease
- untreated celiac disease
- surgery of the pancreas or upper gastrointestinal tract
- Sjogren’s syndrome
- a history of smoking or drinking alcohol
Who is more likely to have EPI?
People who have advanced pancreatic diseases are more likely to develop EPI. For example, EPI is more common in people who have
- chronic and acute pancreatitis
- cystic fibrosis
- pancreatic cancer
- surgery of the pancreas or upper gastrointestinal tract
What are the complications of EPI?
In EPI, the small intestine doesn’t digest food as it should and may not absorb enough nutrients—a condition called malabsorption. EPI and malabsorption can lead to complications such as
- malnutrition
- low levels of fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K in the body
- low bone mass, called osteopenia, and osteoporosis
- problems with growth in children
- weakness of the immune system
- increased risk of cardiovascular events, such as heart attack and stroke
Reference
This content is provided as a service of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
(NIDDK), part of the National Institutes of Health. NIDDK translates and disseminates research findings to increase knowledge and understanding about health and disease among patients, health professionals, and the public. Content produced by NIDDK is carefully reviewed by NIDDK scientists and other experts.